marijuana growing
Mastering Germination of Skunk Marijuana Seeds: A Complete Guide
Published
7 months agoon
By
admin
Germination is the process by which a seed begins to develop into a new plant. It involves activating the dormant seed embryo, enabling it to sprout roots and grow into a full-fledged plant. For skunk marijuana seeds, germination is a crucial step that determines the success of your cultivation journey.
Germination ensures seed viability, unlocks genetic potential, offers control over early growth stages, and facilitates a uniform crop. In this article, we will explore the step-by-step process of germinating skunk marijuana seeds, providing you with the knowledge and techniques required for a successful cultivation experience.

Initiating Germination:
To successfully germinate skunk marijuana seeds, specific conditions need to be met. Let’s dive into the process and understand the key elements involved.
Soak the Skunk Marijuana Seeds: Before proceeding with germination, it’s essential to soak the skunk marijuana seeds in water for approximately 24 hours. This step helps break the dormancy of the seeds and initiates the germination process. Ensure the seeds are fully submerged in water and allow them to absorb moisture. Soaking the seeds also serves as an initial viability test. Healthy seeds will sink in water, indicating their potential for sprouting, while non-viable seeds tend to float. By identifying viable seeds, you can select the best candidates for cultivation and avoid wasting time and resources on non-viable ones.
Preparing the Germination Environment: After soaking the seeds, it’s time to prepare the germination environment. The following steps will help create the optimal conditions for successful sprouting: a) Dampen the Paper Towels: Take a few sheets of paper towel and dampen them with water. It’s crucial to strike a balance between moist and overly wet. Excess moisture can lead to issues like rot or mold, which can harm the seeds. Ensure the paper towels are adequately moist throughout but not dripping with water.
b) Place the Seeds on Damp Paper Towels: Evenly space the soaked skunk marijuana seeds on one half of the damp paper towel. Gently fold the other half over the seeds, creating a sandwich-like structure. This technique helps maintain moisture around the seeds, providing an environment conducive to germination.

c) Create a Mini Greenhouse: Find a container or dish that can accommodate the paper towel with seeds. The container should have a lid or cover to maintain the desired humidity levels. This enclosed space acts as a “mini greenhouse,” promoting the retention of moisture and creating an optimal environment for germination.
Providing the Right Conditions: The success of germination depends on providing the right conditions for the seeds to sprout. Pay attention to the following factors: a) Temperature: Choose a warm location to store the container with the seeds. Ideally, maintain a temperature range between 70°F to 85°F (21°C to 29°C). This warmth expedites the germination process, but extreme temperatures can negatively impact seed viability. Aim for a consistent and moderate temperature.
b) Darkness: Place the container in a dark area or cover it with an opaque material to prevent exposure to light. Darkness plays a crucial role in the germination process as it mimics the seeds’ natural environment. Light can inhibit germination and cause the seeds to remain dormant.
At this point, you have successfully initiated the germination process for your skunk marijuana seeds. But successful germination doesn’t stop here; the subsequent steps and care taken after sprouting significantly impact the growth of your seedlings.
Advanced Germination Techniques:
To further enhance your germination process, consider using advanced techniques like seedling heat mats and germination domes.
a) Seedling Heat Mats: To ensure a consistent temperature, consider using seedling heat mats. These devices provide a warm base for your containers, helping to maintain optimal heat levels and promote faster germination.
b) Germination Domes: Germination domes work in a similar way to your DIY “mini greenhouse” but are purpose-built for germinating seeds. They maintain consistent humidity levels and provide enough space for the emerging seedlings to grow.
Transplanting the Sprouts:
Once you notice the root tips – known as taproots – emerging from the seeds (usually within 2-7 days), it’s time to carefully transplant them into your chosen growing medium. This could be a traditional soil setup, a coco coir-based medium, or a hydroponic system.
Each growing medium has its own benefits. Soil is the most common choice, being rich in nutrients and providing a forgiving environment for novice growers. Coco coir, on the other hand, is a reusable, pH-neutral medium that’s excellent at retaining water and promoting robust root growth. Hydroponic systems, while more complex, allow for precise control over nutrient intake, potentially leading to faster growth and higher yields.

The process of transplanting must be handled with extreme care. Remember, these sprouts are incredibly fragile at this stage. Begin by preparing small holes in your chosen medium, approximately half an inch deep. Using tweezers or a similar tool, gently pick up the germinated seeds by the seed shell, avoiding touching the delicate taproot. Place the sprout in the hole, taproot down, and lightly cover it with your medium.
After transplanting, provide the sprouts with a warm and humid environment. Maintain temperatures around 68°F-77°F (20°C-25°C) and a relative humidity of 70%-90%. During this stage, young marijuana plants don’t require intense light, so opt for a weaker light source to prevent overwhelming them.
Regularly monitor your sprouts, checking for any signs of disease or nutrient deficiencies. A successful transplantation process lays the foundation for healthy, vigorous plants and abundant harvests.
With careful preparation and attention to detail, germinating skunk marijuana seeds can be an incredibly rewarding endeavor. The journey from a dormant seed to a flourishing plant is filled with anticipation and excitement. By following the steps and techniques detailed in this guide, you are well on your way to successfully kick-starting your cannabis cultivation journey. Remember, patience and attentiveness are key during the germination and transplantation processes. Good luck, and happy growing!
Please note: Ensure you are aware of and comply with your local laws and regulations regarding the cultivation of cannabis. Cultivating cannabis may be subject to legal restrictions in some areas.
FAQ
1. How can I successfully germinate skunk marijuana seeds?
To successfully germinate skunk marijuana seeds, soak them in water for about 24 hours to break dormancy. Then, dampen paper towels and place the seeds on one half, folding the other half over them to maintain moisture. Place the paper towel with the seeds in a covered container to create a mini greenhouse. Store the container in a warm, dark location (between 21°C and 29°C) to mimic their natural environment.
2. What advanced techniques can enhance the germination process for marijuana seeds?
Consider using seedling heat mats, which provide consistent warmth to containers and promote faster germination. Germination domes are also useful as they maintain consistent humidity levels and offer space for seedlings to grow.
3. How should I transplant sprouted skunk marijuana seeds?
When transplanting sprouted seeds, prepare small holes in the growing medium, about half an inch deep. Gently pick up the sprouted seeds by the seed shell using tweezers, avoiding the delicate taproot. Place the sprout taproot down in the hole and lightly cover it with the medium. After transplanting, maintain a warm and humid environment (20°C to 25°C with 70% to 90% humidity) and use a weaker light source to avoid overwhelming the young plants.
Disclaimer: This content is meant for educational purposes only. It has been compiled with research from external sources. it is not meant to substitute any medical or legal advice. Please see your local laws for the legality of cannabis use.
Cannabis
Cannabis And Co2 – How To Increase Your Yield
Published
3 months agoon
December 27, 2024By
admin
Discover Cannabis and CO2
Did you know that your plants can be harmed if they don’t get an adequate supply of CO2? Or that an excessive supply of carbon dioxide can potentially be harmful to your marijuana plants? Carbon dioxide is a crucial aspect of marijuana cultivation that can hinder or permanently halt the progress of plant growth. When it comes to supplying your plants with additional carbon dioxide, there are certain factors you need to keep in mind. In this piece “Cannabis and CO2” we will share ways to optimize CO2 levels for cannabis growth.

Why is carbon dioxide essential for cannabis cultivation?
It is essential to ensure that your plants receive a carbon dioxide level above 250 parts per million (ppm). Any CO2 level below this measure can pose immense risk to them. On the other hand, exposing your plants to dangerously high levels of carbon dioxide can be lethal. But why is carbon dioxide essential for cannabis cultivation? It enables plants to complete the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the conversion of carbon dioxide into energy in plants. As the name and formula imply, CO2 consists of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. This is significant because plants require 17 essential elements to grow and reproduce, and hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen make up 95% of a plant’s dry weight.
Many farmers suggest that adding CO2 to the cultivation room could improve yields by up to 20%. However, this guide will show you how to optimize carbon dioxide levels for better weed growth and excellent results.
How to introduce additional CO2 to your garden
There are several methods to add carbon dioxide to your garden. However, many of these methods do not guarantee controlled delivery of the desired PPM. Therefore, we recommend investing in reliable equipment to ensure proper CO2 supplementation.
CO2 generators
CO2 generators offer an effective way to improve the carbon dioxide levels in your plants. These products, resembling outdoor heaters, burn propane or natural gas to produce carbon dioxide. They also emit heat, making them suitable for larger spaces and climate-controlled enclosures.
Compressed CO2
Compressed CO2, stored in metal tanks like propane cylinders or scuba tanks, can be delivered to your plants through emitters. Unlike generating carbon dioxide on your own, compressed carbon dioxide is produced at a factory, eliminating concerns about heat generation. This makes compressed CO2 an excellent choice for small-scale growers.
What does carbon dioxide do for your cannabis plants?
Optimizing carbon dioxide levels for your plants will result in increased growth speed and higher yields. With accelerated growth, you can enjoy bountiful harvests every year, resulting in bigger and better yields without experiencing dry periods. When carbon dioxide is used properly, it increases the moisture content in your plants and enhances their resilience. This enables plants to withstand higher temperatures than they normally would without drying out quickly. As a result, your plants will thrive in hotter conditions, leading to improved growth.

Why use CO2 in cannabis cultivation?
There are two primary benefits of using CO2 in your marijuana plants: faster growth and greater yield. Additionally, plants store a certain amount of moisture and energy in their leaves, and carbon dioxide helps release that energy, allowing plants to blossom. Most cultivators agree that unlocking this stored energy can lead to a 20-30% increase in yield, along with a relative growth speed increase of at least 15%.
What do you need to know before adding CO2 to your cannabis plants?
Adding CO2 will increase the humidity of your cannabis garden, creating a more moist environment. However, higher moisture levels can also increase the risk of fungus and rot. Moreover, uncontrolled release of carbon dioxide can create a toxic environment for both your cannabis plants and yourself. A CO2 level of about 2000 ppm can harm your plants, and levels higher than that can be unsafe for animals and humans to breathe. It’s important to remember that a quantity below 250 ppm will harm your plants.
Since carbon dioxide is heavier than oxygen, it needs to rain down on your plants. Therefore, it’s necessary to regulate carbon dioxide levels to maximize its benefits without sacrificing the oxygen your plants require, and vice versa. In a nutshell, carbon dioxide supplementation will lead to bigger, improved, and higher annual yields.
Cannabis Seeds
Compare Indica Vs Sativa: Differences And Benefits Explained
Published
4 months agoon
December 11, 2024By
admin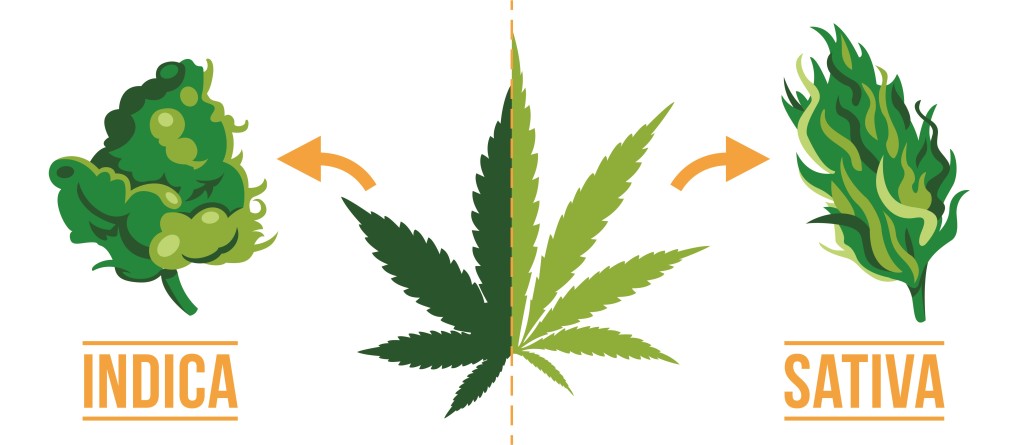
Indica vs Sativa
Who would have thought that in marijuana there are different types of plants with completely different effects and benefits? The origin, the climate, the effects, and the physical characteristics are crucial in order, to differentiate the type of plant that you are going to use either in the clinical, pharmaceutical, or recreational field, as well as to know between Cannabis Sativa and Cannabis Indica in order, to be able to make the best selection of seeds according to your needs.
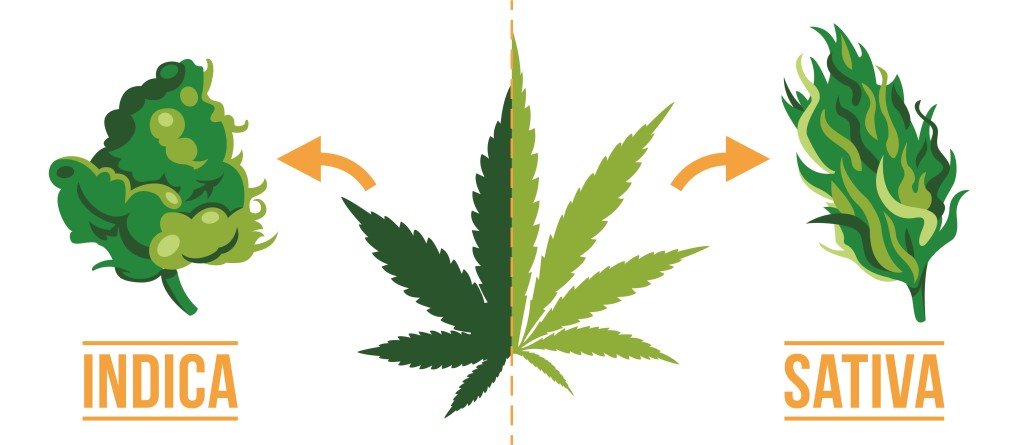
Marijuana is a well-known plant for its mind and body effects and it’s split into two main types: Sativa and Indica. Even though they come from the same family and have similar ingredients, they’re different in how they look and what they do when you use them. Let’s break it down simply:
What the plants look like:
Indica: This plant is short and looks like a bush with wide leaves. It grows well in cooler and mountainous areas.
Sativa: This one is tall and thin, with skinny, pointed leaves, kind of like a young pine tree. It likes hot and humid places.
How they make you feel:
Indica: It chills you out and can make you sleepy, like when you’re getting cozy in bed after a long day.
Sativa: It energizes you and wakes up your mind, great for when you need to do things that require imagination or when you’re hanging out with friends.
To put it simply: if you want to relax, go for Indica. If you want to be more alert and active, go for sativa. We’ll explain more about this soon so you can better understand how each one affects people differently.
The two subspecies of marijuana represent different adaptations to different climates. Sativa originates from the jungles of equatorial regions such as Thailand, Cambodia, Jamaica, Colombia, and Mexico, places that enjoy long hours of sunshine and constant light throughout the year. The Indica variety, on the other hand, comes from the Hindu Kush region, a vast mountain range of more than 800 kilometers that stretches from Afghanistan to China and is characterized by a very cold climate.
Climatic and physical characteristics
Cannabis Sativa is known for its ability to adapt to the heat of tropical climates, being resistant to low temperatures and showing an effective ability to prevent the growth of fungi commonly associated with humidity. Indicas, on the other hand, originate from mountainous climates, which enables them to withstand climatic challenges such as wind, rain, and frost.
Morphology and appearance:
Morphology of Cannabis Sativa
Cannabis Sativa plants, are distinguished by their unique morphology and appearance, which tend to be taller and more slender, with long, thin leaves, differentiating them from other marijuana species such as Indica and Ruderalis. The following points highlight the main morphological and appearance characteristics of Sativa:
- Height and Structure: Cannabis sativa plants are typically tall and slender, with some varieties reaching heights of up to 20 feet (about 6 meters) under optimal conditions. They have a more open structure compared to the bushier Cannabis indica, allowing for greater light penetration throughout the plant.
- Leaves: The leaves of Cannabis sativa are characteristically long and narrow with a light green color. They possess serrated edges and are composed of slender leaflets that are spread far apart. The number of leaflets can vary, usually between 5 to 13 per leaf.
- Branching: Sativa plants have less dense branching compared to their indica counterparts, with branches extending outward and upward, giving the plant an airy appearance. This less compact structure is beneficial for air circulation and can help in reducing the risk of mold and fungal diseases in humid environments.
- Flowers (Buds): The flowers of Cannabis sativa are elongated and less dense than those of indica plants. They tend to be more “fluffy” or airy and can appear on the plant as spaced, apart clusters. The flowering period for sativa strains is generally longer, often taking between 10 to 16 weeks to fully mature.
- Trichomes: While both sativa and indica plants produce trichomes (the resinous glands containing cannabinoids), the concentration and distribution can vary. Sativa plants typically have a high concentration of trichomes on the flowers and surrounding foliage, contributing to their potent therapeutic and psychoactive properties.
- Root System: Cannabis sativa plants develop a deep taproot system, which enables them to access water from deeper soil layers. This characteristic is beneficial for plants growing in arid conditions, allowing them to thrive where other plants might not.
- Growth Pattern and Maturation: Sativa strains usually have a longer vegetative growth phase, which contributes to their tall stature. Their extended flowering time requires patience but can result in high yields of marijuana flowers.
Cannabis sativa strains are often associated with a cerebral, uplifting high, attributed to their higher concentration of THC in comparison to CBD. This makes them particularly popular for daytime use. The distinct morphology and appearance of sativa not only contribute to its cultivation requirements but also influence its effects and applications, making it a fav
Morphology of Cannabis Indica
Cannabis Indica plants have distinctive morphological traits, shorter and more compact appearance, with wider and denser leaves, traits that differentiate from Sativa and Ruderalis. The main characteristics of Indica are described below:
- Height and Structure: Cannabis indica plants are generally shorter and bushier than their sativa counterparts, typically reaching heights of 2 to 4 feet (about 0.6 to 1.2 meters). They have a compact, dense structure, which makes them well-suited for indoor cultivation.
- Leaves: The leaves of Cannabis indica are broad and dark green, with fewer but wider leaflets compared to sativa plants. Indica leaves often have between 7 to 9 leaflets, which are closer together, giving the leaf a fuller appearance.
- Branching: Indica plants have dense branching, with closer internodal spaces. This compact growth habit results in a bushy appearance and contributes to their ability to produce more buds in a smaller space.
- Flowers (Buds): The buds of Cannabis indica plants are typically dense, thick, and bulky, clustering around the plant’s nodes. Due to the plant’s compact nature, these buds are often heavier and more resinous than those of sativa strains, leading to higher yields per square foot in controlled environments.
- Trichomes: Cannabis indica plants are known for their abundant trichome production, which covers the buds and surrounding foliage in a thick layer of crystalline resin. This resin is rich in cannabinoids like THC and CBD, making indica strains highly potent.
- Root System: Indica plants have a more spread-out root system compared to the deep taproot of sativa plants. This characteristic makes them more adaptable to various growing mediums and efficient in nutrient uptake from the soil.
- Growth Pattern and Maturation: Cannabis indica strains have a shorter vegetative growth phase and a faster flowering cycle than sativa strains, often maturing in 6 to 8 weeks. This quick turnaround makes them attractive to cultivators looking for a fast crop.
- Effects: Indica strains are traditionally associated with a sedative, body-centric effect, often referred to as a “body high.” This makes them popular for evening use, providing relaxation and aiding in sleep.
The morphology and appearance of Cannabis indica are not just significant for identification; they also have practical implications for cultivation and use. The compact, dense growth of indica plants makes them particularly suited for indoor or space-constrained environments. Their potent, resinous buds are favored for their strong therapeutic effects, offering relief from pain, anxiety, insomnia, and more.
Chemical and Psychoactive Composition
Both subspecies contain a variety of chemical compounds, but the proportions of these compounds can vary.
Cannabis Sativa: Sativas tend to have higher levels of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the compound responsible for the psychoactive effects. They may also contain significant amounts of cannabidiol (CBD), which has health properties, but in lower proportions than THC.
Cannabis Indica: Indicas generally have slightly lower THC levels than Sativas, but can still be potent. They tend to have a more balanced ratio of THC and CBD, which can result in a more relaxing and sedative effect.
When it comes to psychoactive effects, it is important to remember that although both Sativa and Indica contain THC, the effects and reactions vary greatly depending on the type of plant.
So which strain is right for me? Amsterdam Marijuana Seeds can tell you:
Sativa is known for its properties that induce a state of euphoria and greater sociability compared to the Indica variety. This sub-species enhances perception, intensifying the appreciation of colors and sounds while stimulating creativity and thinking. Sativa is used to relieve stress, anxiety, depression, nausea, migraines, and as an appetite stimulant, among other wellness benefits.
On the other hand, Indica, known for its relaxing and sedative properties, is highly effective in the treatment of insomnia and a variety of conditions. It is widely used to alleviate neuromuscular disorders such as tremors and, spasms, and to combat chronic pain. It is also a valuable option for reducing anxiety and stress and stimulating appetite in patients who need it.
Alternative uses
Cannabis Sativa: Sativas are often used to treat depression, anxiety and to improve mood. They can also be useful in treating attention deficit disorder and stimulating appetite.
Cannabis Indica: Indicas are preferred for the treatment of chronic pain, insomnia, anxiety and to relax tense muscles. They are also commonly used to treat gastrointestinal disorders.
It is important to note that due to hybridisation and genetic variability of marijuana strains, classification as sativa or indica is not always accurate. In addition, individual experience with these subspecies may vary between individuals and specific strains.
Sativa and Indica are two subspecies with marked differences in morphology, chemical composition, psychoactive effects, and alternative uses. The choice between one or the other depends on the personal preferences and therapeutic needs of each individual.
Cannabis Seeds
Marijuana Seed Varieties For Cultivation
Published
4 months agoon
December 8, 2024By
admin
CBD Seeds
CBD marijuana seeds share characteristics with feminized, regular, or autoflowering varieties, but are distinguished by their higher CBD content compared to conventional varieties. Additionally, in many cases, the aim is to minimize the THC level so that they can be used for medicinal purposes.
However, these seeds never contain the adequate concentration of THC for use in legal CBD product production, which currently must be below 0.2%. For this purpose, hemp seeds are used. Despite this, CBD marijuana seed varieties still offer more relaxing and stress-relieving effects than other varieties.
Hemp Seeds
Unlike CBD seeds, hemp seeds always contain THC levels below 0.2%, ensuring a predominance of CBD. Also known as industrial hemp, this variety is used for CBD extraction and the production of therapeutic products. However, the CBD levels obtained from hemp never reach those achieved with CBD seeds.
Hemp seeds are not only used for obtaining cannabidiol but also for extracting strong fibers used in various industries, such as textile, paper, insulation, rope manufacturing, fuel, paints, cosmetics, among others. Additionally, hemp seeds are edible and can be consumed as oil, whole, raw, toasted, or ground into flour.
Fast Version Seeds
Like CBD marijuana seeds, Fast Version seeds have similar characteristics to regular or feminized varieties, but their life cycle is shorter than usual, allowing for harvesting before the first October frosts.
Indeed, many of these types of seeds can be combined. Sativa, indica, hybrid, or ruderalis varieties can be presented in feminized, regular, autoflowering, or Fast Version forms. Hemp seeds, on the other hand, belong to the sativa group.

The best energizing THC gummies of 2025 by Leafly

Mixed Messages From The Feds About Cannabis

How Hemp Helps You Sleep

420 in Texas is at Reggie & Dro

Daily Cannabis Use Can Help People Get Off Opioids (STUDY)

This Wine Issue Is Becoming More Common

Get more for less this 420 at PurLife

Can You Order Cannabis through DoorDash?

Cannabis Enthusiast-Friendy Retreats – GanjaVacations Jamaica

The road ahead for cannabis lending in 2025

Distressed Cannabis Business Takeaways – Canna Law Blog™

United States: Alex Malyshev And Melinda Fellner Discuss The Intersection Of Tax And Cannabis In New Video Series – Part VI: Licensing (Video)

What you Need to Know

Drug Testing for Marijuana – The Joint Blog

NCIA Write About Their Equity Scholarship Program

It has been a wild news week – here’s how CBD and weed can help you relax

Cannabis, alcohol firm SNDL loses CA$372.4 million in 2022

A new April 20 cannabis contest includes a $40,000 purse

Your Go-To Source for Cannabis Logos and Designs

UArizona launches online cannabis compliance online course
Trending
-

 Cannabis News2 years ago
Cannabis News2 years agoDistressed Cannabis Business Takeaways – Canna Law Blog™
-

 One-Hit Wonders2 years ago
One-Hit Wonders2 years agoUnited States: Alex Malyshev And Melinda Fellner Discuss The Intersection Of Tax And Cannabis In New Video Series – Part VI: Licensing (Video)
-

 Cannabis 1012 years ago
Cannabis 1012 years agoWhat you Need to Know
-

 drug testing1 year ago
drug testing1 year agoDrug Testing for Marijuana – The Joint Blog
-

 Education2 years ago
Education2 years agoNCIA Write About Their Equity Scholarship Program
-

 Cannabis2 years ago
Cannabis2 years agoIt has been a wild news week – here’s how CBD and weed can help you relax
-

 Marijuana Business Daily2 years ago
Marijuana Business Daily2 years agoCannabis, alcohol firm SNDL loses CA$372.4 million in 2022
-

 California2 years ago
California2 years agoA new April 20 cannabis contest includes a $40,000 purse









