Cannabis Seeds
Learn About Fast Flowering Cannabis Strains and Seeds
Published
2 years agoon
By
admin
Fast-flowering strains combine photoperiod genetics with autoflowering genetics. They have been engineered to grow and mature faster than traditional cannabis plants. This means quicker harvests and increased yields compared to autoflower strains. Fast flowering strain yields can match those of photoperiod cannabis varieties.
Understanding fast flowering weed and how it differs from established photoperiod and autoflower cultivars is key for growers of any level. This article’ll dive deeper into these differences, how fast-flowering cultivars are made, and their added benefits.
ILGM has seeds on offer regularly! Sign up below to stay posted on the latest deals.
The difference between fast-flowering and autoflowers
The primary difference between fast-flowering cannabis variants and autoflowering cannabis variants is how they flower. Fast-flowering variants are photoperiod dependent (they need light manipulation to flower and mature). The light cycle will need to be turned back or “flipped” from 18 hours on and 6 hours off to 12 hours on and 12 hours off for the plants to transition from their vegetative stage into their flowering stage.
This is in contrast to autoflowering strains, which automatically go into their flowering period within 4-6 weeks of germination from seed. Thus, fast-flowering cultivars give growers the benefits of sturdy and potent photoperiod strains in a shorter period of time.

Buy Fast-Flowering Seeds
- 2-5 weeks faster than normal seeds
- High-quality feminized genetics
- Delivery and germination guaranteed
How fast-flowering strains are made
There has been a surge in the development of fast-flowering strains due to the increased demand for cannabis products. Breeders utilize selective genetics and hybridization techniques to produce these fast version strains. In the case of fast-flowering cultivars, the breeders selected genetics from plants that flowered faster than some of their sisters.
Sometimes, fast-flowering cannabis varieties are made by introducing photoperiod plants to pollen from autoflower plants. This introduces even more fast-flowering genetic traits to the new phenotype (strain). After that, breeders stabilize the Ruderalis genetics by reintroducing photoperiod genetics through a process called “back-crossing”.
This produces fast-flowering, photoperiod-dependent, and cloneable cultivars.
Growing fast-flowering strains
One of the significant advantages of growing fast-flowering cannabis strains is that they’ll reach the flowering phase quicker than traditional light-cycle dependent strains. The flowering time for these strains can range from 6-8 weeks, while many traditional photoperiod strains can take 7 -to 10 weeks or longer.
The shorter flowering period allows growers to turn over more crops. Additionally, fast-flowering strains can be grown multiple times a year in the same space, potentially increasing yields and profits.
Fast-flowering strains can have a longer period of vegetative growth and training if desired, giving growers more options.
Pros and cons of fast-flowering strains
Besides the reduced growth cycle time, fast-flowering plants are also more resistant to pests and diseases than traditional strains. This is likely because they mature quicker, leaving less time for diseases and pests to take hold.
Fast-flowerers are also more resistant to environmental factors such as temperature changes and extreme weather conditions, making them easier to grow in a wider range of locations. The shorter growing times also allow for more potential harvests on a yearly basis.
While fast-flowering strains have many advantages, they also have some drawbacks. One of the main disadvantages is a potentially smaller yield than traditional strains. Lower yields occur because these strains complete their life cycle much quicker than traditional strains. That means they have less time to develop and grow. Additionally, fast-flowering strains may produce lower levels of THC and other cannabinoids than traditional strains.
Fast-flowering strains may also require more immediate attention from growers due to their shorter lifespan. Any potential errors or mistakes may mean extending the growth cycle or delaying flowering for the plants to recover.
Are fast flowering strains good?
This is a tough question to answer. It all depends on what you consider “good”. Fast-flowering strains are a good option for growers looking for decent yields of potent flowers in less time than photo cultivars take. But, due to shorter growth cycles, as I stated before, the yield might not be as high as with ‘regular’ photoperiod plants, which get all the time they need to fully flourish.
Fast-flowering cultivars also offer more customization for growing and training than autoflowers, as well as more time to recover from any potential mistakes or accidents that might occur.
So, yes. Ultimately, fast-flowering cultivars are “good” if you want training flexibility and production speed with a decent and potent yield compared to most autoflower varieties. But if you’re looking for fully optimized yields, our feminized photoperiod options are a ‘better choice.’
What is the fastest-growing cannabis strain?
There may be some debate as to which cannabis strains grow the fastest. Afghani and Skunk strains tend to be the fastest-growing from what I’ve experienced. However, those were regular photoperiod cultivars.
When you look online, pretty much every site has its own lists, each with different strains of claiming to be the fastest. But are those claims justified? It’s hard to say since no one has really tested it. The only thing we can say for certain is that autoflowering seeds can be harvested earlier than many of their photoperiod counterparts. And when it comes to subspecies, sativa tends to need longer than indica plants.
Check out our list of fast flowering strains to see which ones we think are our fastest. And if you’re new to growing or just want some great information on enhancing your current skills, download Robert’s free Grow Bible here.
You may like
Cannabis Seeds
Compare Indica Vs Sativa: Differences And Benefits Explained
Published
3 months agoon
December 11, 2024By
admin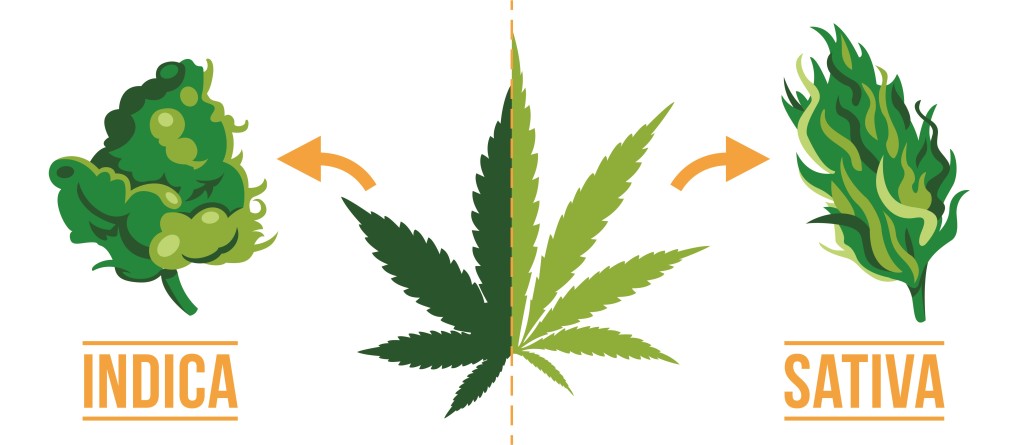
Indica vs Sativa
Who would have thought that in marijuana there are different types of plants with completely different effects and benefits? The origin, the climate, the effects, and the physical characteristics are crucial in order, to differentiate the type of plant that you are going to use either in the clinical, pharmaceutical, or recreational field, as well as to know between Cannabis Sativa and Cannabis Indica in order, to be able to make the best selection of seeds according to your needs.
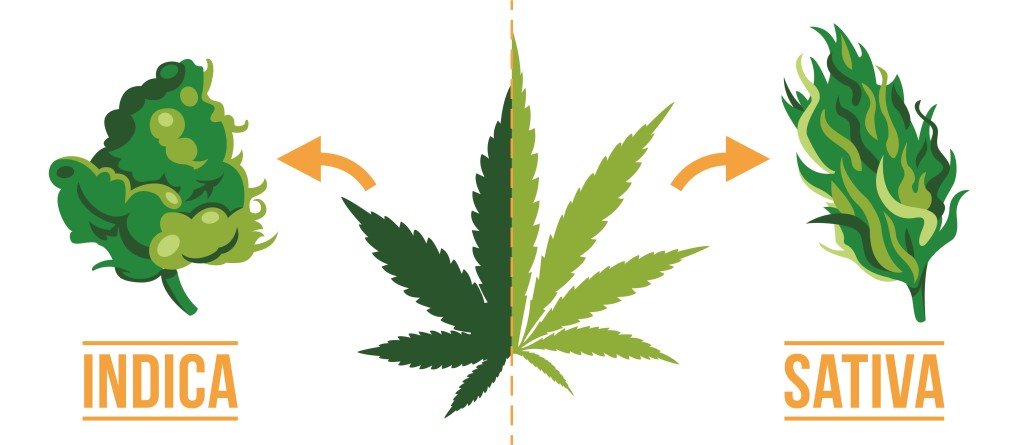
Marijuana is a well-known plant for its mind and body effects and it’s split into two main types: Sativa and Indica. Even though they come from the same family and have similar ingredients, they’re different in how they look and what they do when you use them. Let’s break it down simply:
What the plants look like:
Indica: This plant is short and looks like a bush with wide leaves. It grows well in cooler and mountainous areas.
Sativa: This one is tall and thin, with skinny, pointed leaves, kind of like a young pine tree. It likes hot and humid places.
How they make you feel:
Indica: It chills you out and can make you sleepy, like when you’re getting cozy in bed after a long day.
Sativa: It energizes you and wakes up your mind, great for when you need to do things that require imagination or when you’re hanging out with friends.
To put it simply: if you want to relax, go for Indica. If you want to be more alert and active, go for sativa. We’ll explain more about this soon so you can better understand how each one affects people differently.
The two subspecies of marijuana represent different adaptations to different climates. Sativa originates from the jungles of equatorial regions such as Thailand, Cambodia, Jamaica, Colombia, and Mexico, places that enjoy long hours of sunshine and constant light throughout the year. The Indica variety, on the other hand, comes from the Hindu Kush region, a vast mountain range of more than 800 kilometers that stretches from Afghanistan to China and is characterized by a very cold climate.
Climatic and physical characteristics
Cannabis Sativa is known for its ability to adapt to the heat of tropical climates, being resistant to low temperatures and showing an effective ability to prevent the growth of fungi commonly associated with humidity. Indicas, on the other hand, originate from mountainous climates, which enables them to withstand climatic challenges such as wind, rain, and frost.
Morphology and appearance:
Morphology of Cannabis Sativa
Cannabis Sativa plants, are distinguished by their unique morphology and appearance, which tend to be taller and more slender, with long, thin leaves, differentiating them from other marijuana species such as Indica and Ruderalis. The following points highlight the main morphological and appearance characteristics of Sativa:
- Height and Structure: Cannabis sativa plants are typically tall and slender, with some varieties reaching heights of up to 20 feet (about 6 meters) under optimal conditions. They have a more open structure compared to the bushier Cannabis indica, allowing for greater light penetration throughout the plant.
- Leaves: The leaves of Cannabis sativa are characteristically long and narrow with a light green color. They possess serrated edges and are composed of slender leaflets that are spread far apart. The number of leaflets can vary, usually between 5 to 13 per leaf.
- Branching: Sativa plants have less dense branching compared to their indica counterparts, with branches extending outward and upward, giving the plant an airy appearance. This less compact structure is beneficial for air circulation and can help in reducing the risk of mold and fungal diseases in humid environments.
- Flowers (Buds): The flowers of Cannabis sativa are elongated and less dense than those of indica plants. They tend to be more “fluffy” or airy and can appear on the plant as spaced, apart clusters. The flowering period for sativa strains is generally longer, often taking between 10 to 16 weeks to fully mature.
- Trichomes: While both sativa and indica plants produce trichomes (the resinous glands containing cannabinoids), the concentration and distribution can vary. Sativa plants typically have a high concentration of trichomes on the flowers and surrounding foliage, contributing to their potent therapeutic and psychoactive properties.
- Root System: Cannabis sativa plants develop a deep taproot system, which enables them to access water from deeper soil layers. This characteristic is beneficial for plants growing in arid conditions, allowing them to thrive where other plants might not.
- Growth Pattern and Maturation: Sativa strains usually have a longer vegetative growth phase, which contributes to their tall stature. Their extended flowering time requires patience but can result in high yields of marijuana flowers.
Cannabis sativa strains are often associated with a cerebral, uplifting high, attributed to their higher concentration of THC in comparison to CBD. This makes them particularly popular for daytime use. The distinct morphology and appearance of sativa not only contribute to its cultivation requirements but also influence its effects and applications, making it a fav
Morphology of Cannabis Indica
Cannabis Indica plants have distinctive morphological traits, shorter and more compact appearance, with wider and denser leaves, traits that differentiate from Sativa and Ruderalis. The main characteristics of Indica are described below:
- Height and Structure: Cannabis indica plants are generally shorter and bushier than their sativa counterparts, typically reaching heights of 2 to 4 feet (about 0.6 to 1.2 meters). They have a compact, dense structure, which makes them well-suited for indoor cultivation.
- Leaves: The leaves of Cannabis indica are broad and dark green, with fewer but wider leaflets compared to sativa plants. Indica leaves often have between 7 to 9 leaflets, which are closer together, giving the leaf a fuller appearance.
- Branching: Indica plants have dense branching, with closer internodal spaces. This compact growth habit results in a bushy appearance and contributes to their ability to produce more buds in a smaller space.
- Flowers (Buds): The buds of Cannabis indica plants are typically dense, thick, and bulky, clustering around the plant’s nodes. Due to the plant’s compact nature, these buds are often heavier and more resinous than those of sativa strains, leading to higher yields per square foot in controlled environments.
- Trichomes: Cannabis indica plants are known for their abundant trichome production, which covers the buds and surrounding foliage in a thick layer of crystalline resin. This resin is rich in cannabinoids like THC and CBD, making indica strains highly potent.
- Root System: Indica plants have a more spread-out root system compared to the deep taproot of sativa plants. This characteristic makes them more adaptable to various growing mediums and efficient in nutrient uptake from the soil.
- Growth Pattern and Maturation: Cannabis indica strains have a shorter vegetative growth phase and a faster flowering cycle than sativa strains, often maturing in 6 to 8 weeks. This quick turnaround makes them attractive to cultivators looking for a fast crop.
- Effects: Indica strains are traditionally associated with a sedative, body-centric effect, often referred to as a “body high.” This makes them popular for evening use, providing relaxation and aiding in sleep.
The morphology and appearance of Cannabis indica are not just significant for identification; they also have practical implications for cultivation and use. The compact, dense growth of indica plants makes them particularly suited for indoor or space-constrained environments. Their potent, resinous buds are favored for their strong therapeutic effects, offering relief from pain, anxiety, insomnia, and more.
Chemical and Psychoactive Composition
Both subspecies contain a variety of chemical compounds, but the proportions of these compounds can vary.
Cannabis Sativa: Sativas tend to have higher levels of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the compound responsible for the psychoactive effects. They may also contain significant amounts of cannabidiol (CBD), which has health properties, but in lower proportions than THC.
Cannabis Indica: Indicas generally have slightly lower THC levels than Sativas, but can still be potent. They tend to have a more balanced ratio of THC and CBD, which can result in a more relaxing and sedative effect.
When it comes to psychoactive effects, it is important to remember that although both Sativa and Indica contain THC, the effects and reactions vary greatly depending on the type of plant.
So which strain is right for me? Amsterdam Marijuana Seeds can tell you:
Sativa is known for its properties that induce a state of euphoria and greater sociability compared to the Indica variety. This sub-species enhances perception, intensifying the appreciation of colors and sounds while stimulating creativity and thinking. Sativa is used to relieve stress, anxiety, depression, nausea, migraines, and as an appetite stimulant, among other wellness benefits.
On the other hand, Indica, known for its relaxing and sedative properties, is highly effective in the treatment of insomnia and a variety of conditions. It is widely used to alleviate neuromuscular disorders such as tremors and, spasms, and to combat chronic pain. It is also a valuable option for reducing anxiety and stress and stimulating appetite in patients who need it.
Alternative uses
Cannabis Sativa: Sativas are often used to treat depression, anxiety and to improve mood. They can also be useful in treating attention deficit disorder and stimulating appetite.
Cannabis Indica: Indicas are preferred for the treatment of chronic pain, insomnia, anxiety and to relax tense muscles. They are also commonly used to treat gastrointestinal disorders.
It is important to note that due to hybridisation and genetic variability of marijuana strains, classification as sativa or indica is not always accurate. In addition, individual experience with these subspecies may vary between individuals and specific strains.
Sativa and Indica are two subspecies with marked differences in morphology, chemical composition, psychoactive effects, and alternative uses. The choice between one or the other depends on the personal preferences and therapeutic needs of each individual.
Cannabis Seeds
Marijuana Seed Varieties For Cultivation
Published
3 months agoon
December 8, 2024By
admin
CBD Seeds
CBD marijuana seeds share characteristics with feminized, regular, or autoflowering varieties, but are distinguished by their higher CBD content compared to conventional varieties. Additionally, in many cases, the aim is to minimize the THC level so that they can be used for medicinal purposes.
However, these seeds never contain the adequate concentration of THC for use in legal CBD product production, which currently must be below 0.2%. For this purpose, hemp seeds are used. Despite this, CBD marijuana seed varieties still offer more relaxing and stress-relieving effects than other varieties.
Hemp Seeds
Unlike CBD seeds, hemp seeds always contain THC levels below 0.2%, ensuring a predominance of CBD. Also known as industrial hemp, this variety is used for CBD extraction and the production of therapeutic products. However, the CBD levels obtained from hemp never reach those achieved with CBD seeds.
Hemp seeds are not only used for obtaining cannabidiol but also for extracting strong fibers used in various industries, such as textile, paper, insulation, rope manufacturing, fuel, paints, cosmetics, among others. Additionally, hemp seeds are edible and can be consumed as oil, whole, raw, toasted, or ground into flour.
Fast Version Seeds
Like CBD marijuana seeds, Fast Version seeds have similar characteristics to regular or feminized varieties, but their life cycle is shorter than usual, allowing for harvesting before the first October frosts.
Indeed, many of these types of seeds can be combined. Sativa, indica, hybrid, or ruderalis varieties can be presented in feminized, regular, autoflowering, or Fast Version forms. Hemp seeds, on the other hand, belong to the sativa group.
Cannabis Seeds
The Mystique Of Purple Weed: Colors, Potency, And Flavor
Published
5 months agoon
October 7, 2024By
admin
Undeniably, purple buds are awesome. Purple cannabis strains have an exotic appearance and often bear cool names like Blue Dream XTRM or Purple Power XTRM. But does their deep purple pigment indicate potency or alter the taste compared to regular green weed? Read on to discover the answers.
Purple or Another Shade of Color
Firstly, let’s explain why certain marijuana strains turn purple or display other colors. The reason lies in their genetic ability to produce anthocyanins. Anthocyanins are a family of flavonoids that generate pigments such as blue, purple, or red. Various fruits and vegetables like eggplants, blueberries, purple grapes, and red cabbage naturally contain anthocyanins. Some marijuana strains possess higher levels of anthocyanins due to their genetic makeup. Since anthocyanins are potent pigment compounds, only a small amount of these flavonoids is required for the plant to exhibit bold colors.
Anthocyanins are found in the vacuoles of cells within the plant’s leaves, flowers, and fruits. These flavonoids can also migrate to the marijuana trichome stalk and even reside inside the trichome head, creating an intriguing visual effect. The presence of anthocyanins in the trichomes adds to the overall appeal of purple cannabis strains.
It is important to note that the color of cannabis plants is not solely limited to purple. Some strains may exhibit shades of blue or red. The final coloration depends on several factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental conditions, and the pH level.
The Role of Genetics and Pigments
The genetic makeup of a marijuana strain plays a significant role in determining the presence and concentration of anthocyanins. Some strains are bred specifically to enhance the expression of these pigments, resulting in vibrant purple hues.
Flavonoids, including anthocyanins, serve multiple purposes in plants. They act as natural sunscreens, protecting photosynthetic tissues from excessive light and UV radiation. In cannabis, anthocyanins help shield the leaves from high light intensities, reducing stress on the plant. These pigments also contribute to antioxidant properties, offering additional protection against environmental stressors.
The production of anthocyanins is influenced by various environmental factors, such as temperature, light exposure, and nutrient availability. Cooler temperatures, particularly during the late stages of flowering, can stimulate anthocyanin production and intensify the coloration of cannabis plants.
The pH level of the plant’s environment also plays a crucial role in determining the color. Anthocyanins respond to changes in pH, exhibiting different shades depending on whether the environment is acidic, neutral, or alkaline. In an acidic environment, the plant tends to display red or pink colors. Neutral environments result in purple hues, while higher pH levels lead to blue shades. Yellow colorization occurs in alkaline environments. Anthocyanin pigments thrive best in an acidic environment, which is why many purple cannabis strains exhibit their vibrant colors under slightly acidic conditions.
Taste and Aroma of Purple Weed
Contrary to popular belief, the taste and aroma of purple weed are primarily determined by the strain rather than the color. While some people expect purple weed to have a grape-like flavor, the reality is that the flavor profile varies greatly among different strains.
Each strain possesses its own unique combination of terpenes, aromatic compounds that contribute to the taste and smell of cannabis. The terpene profile of a strain plays a significant role in determining its flavor characteristics. For example, some purple strains may have fruity or berry-like flavors, while others might exhibit earthy or spicy undertones.
It’s important to note that the taste and aroma of cannabis are subjective experiences that can vary from person to person. What one individual finds appealing, another may not enjoy as much. Therefore, it’s recommended to explore different strains and experiment to find the flavors that suit your palate.
Perception of Potency of Purple Weed
Purple cannabis strains have gained a reputation for being potent and highly desirable among consumers. However, it’s essential to clarify that the color of the bud itself does not directly correlate with its potency. The level of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, is not inherently influenced by the color of the buds.
The potency of a cannabis strain depends on various factors, including specific genetics, cultivation techniques, harvesting, and curing processes. While some purple strains may indeed be potent, it’s crucial to evaluate the overall cannabinoid and terpene profile of the strain to determine its effects and potency accurately.
Additionally, factors such as trichome density, resin production, and overall cannabinoid content contribute to the potency and quality of the cannabis. These characteristics can vary among different strains, regardless of their color.
Rarity and Market Value of Purple Weed
Purple cannabis strains tend to be rarer compared to their green counterparts. The distinctive coloration and unique visual appeal make them sought after by cannabis enthusiasts and collectors. As a result, the market value of purple buds may be higher due to their relative scarcity and aesthetic appeal.
Furthermore, the cultivation process for purple strains can be more challenging and time-consuming. Growers often need to carefully manage environmental conditions, including temperature, light exposure, and nutrient availability, to encourage the expression of anthocyanins. These additional efforts contribute to the higher cost of producing purple cannabis strains, which may be reflected in their price.
The Influence of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in determining the color expression of cannabis plants. Apart from genetics, the following factors can influence the coloration of the buds:
Temperature:
Temperature fluctuations can impact the coloration of cannabis plants. A drop in temperature during the flowering phase can stimulate anthocyanin production and intensify the purple, blue, or red hues. Conversely, higher temperatures may reduce the expression of anthocyanins, resulting in less vibrant colors.
Light Exposure:
The intensity and duration of light exposure can influence color development in cannabis plants. Certain strains may require specific light conditions to maximize the expression of anthocyanins. Adequate exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light during specific stages of growth can enhance the coloration of the buds.
Nutrient Availability:
The availability and balance of essential nutrients can affect the overall health and coloration of cannabis plants. Deficiencies or excesses in certain nutrients can lead to color variations and impact the intensity of pigmentation. Providing optimal nutrient levels, particularly micronutrients, can help promote vibrant color development.
Appreciating the Beauty of Purple Cannabis
Whether you’re a cannabis enthusiast or a casual consumer, purple buds offer a visually striking and captivating experience. The rich hues and vibrant colors add a touch of uniqueness to the cannabis landscape.
It’s worth noting that while the color of the buds may not directly affect their potency or taste, the visual appeal and novelty factor associated with purple strains can enhance the overall enjoyment of the cannabis experience. From aesthetic pleasure to the diverse range of flavors and aromas, exploring different purple strains allows for a deeper appreciation of the plant’s intricacies.

Minnesota: Ishkode cannabis dispensary is now open at Vermilion

Ohio House Republicans’ cannabis measure a ‘slap in face,’ NORML says

Save 30% all month long at The Dispensary Fulton

Ohioans activate to defend weed legalization from lawmakers

It All Turned A Bit Bogan At Aussie Medical Cannabis Symposium

Building cannabis brands that reach across markets

ILGM’s Home Grow Tour 2025

Should Medical Marijuana Be Allowed in Worker’s Comp Claims?

Karma Koala Podcast 238: Daniel Shortt Launches New Firm With Partner Perry Salzhauer In Pacific NW
Trump invites former cannabis prisoner to speech, but doesn’t mention cannabis (Newsletter: February 5, 2025)

Distressed Cannabis Business Takeaways – Canna Law Blog™

United States: Alex Malyshev And Melinda Fellner Discuss The Intersection Of Tax And Cannabis In New Video Series – Part VI: Licensing (Video)

What you Need to Know

Drug Testing for Marijuana – The Joint Blog

NCIA Write About Their Equity Scholarship Program

It has been a wild news week – here’s how CBD and weed can help you relax

Cannabis, alcohol firm SNDL loses CA$372.4 million in 2022

A new April 20 cannabis contest includes a $40,000 purse

Your Go-To Source for Cannabis Logos and Designs

UArizona launches online cannabis compliance online course
Trending
-

 Cannabis News2 years ago
Cannabis News2 years agoDistressed Cannabis Business Takeaways – Canna Law Blog™
-

 One-Hit Wonders2 years ago
One-Hit Wonders2 years agoUnited States: Alex Malyshev And Melinda Fellner Discuss The Intersection Of Tax And Cannabis In New Video Series – Part VI: Licensing (Video)
-

 Cannabis 1012 years ago
Cannabis 1012 years agoWhat you Need to Know
-

 drug testing1 year ago
drug testing1 year agoDrug Testing for Marijuana – The Joint Blog
-

 Education2 years ago
Education2 years agoNCIA Write About Their Equity Scholarship Program
-

 Cannabis2 years ago
Cannabis2 years agoIt has been a wild news week – here’s how CBD and weed can help you relax
-

 Marijuana Business Daily2 years ago
Marijuana Business Daily2 years agoCannabis, alcohol firm SNDL loses CA$372.4 million in 2022
-

 California2 years ago
California2 years agoA new April 20 cannabis contest includes a $40,000 purse



